
Measuring acid volumes accurately is critical in chemistry and research‚ ensuring precise reactions and safe handling. Proper equipment and techniques are essential for reliable results.
1.1 Importance of Accurate Volume Measurement
Accurate measurement of acid volumes is crucial for precise chemical reactions‚ ensuring safety‚ and achieving reliable experimental results. Even minor errors can significantly affect reaction outcomes and safety protocols. Proper techniques and equipment minimize discrepancies‚ preventing potential hazards associated with acid handling. This ensures that experimental data remains consistent and trustworthy‚ especially in titrations and solution preparations where concentration accuracy is vital. Inaccuracies can lead to incorrect concentrations‚ potentially endangering experiments and personnel. Thus‚ understanding and implementing precise measurement practices are fundamental in laboratory settings.
1.2 Overview of Common Laboratory Equipment
Laboratories utilize specific tools for precise acid volume measurement. Pipettes‚ burettes‚ volumetric flasks‚ and graduated cylinders are essential instruments. Each serves distinct purposes‚ with pipettes offering high accuracy for small volumes‚ while burettes are ideal for titrations. Volumetric flasks ensure precise dilutions‚ and graduated cylinders handle larger quantities. These instruments vary in design and function but are critical for maintaining measurement accuracy and safety. Their proper use is fundamental to successful experiments and safe acid handling‚ ensuring reliable and consistent results across various applications.

Pipettes
Pipettes are precise volumetric instruments for measuring and transferring small liquid volumes accurately. They are essential for titrations and dilutions‚ ensuring efficient and accurate acid measurements.
2.1 Types of Pipettes
Pipettes are categorized into different types based on their functionality and volume range. Fixed-volume pipettes deliver a specific volume‚ while variable-volume pipettes allow adjustment within a range. Air-displacement pipettes are common for general use‚ utilizing a piston mechanism. Positive-displacement pipettes are ideal for viscous or hazardous liquids‚ reducing contamination risks. Electronic pipettes offer precise digital control‚ enhancing accuracy. Each type is suited for specific applications‚ ensuring optimal performance in measuring acid volumes efficiently and safely.
2.2 Operating Principles
Pipettes operate on the principle of air displacement to measure and transfer precise liquid volumes. A piston mechanism creates suction‚ drawing liquid into the pipette tip. For fixed-volume pipettes‚ the volume is set during manufacturing‚ while variable-volume pipettes allow adjustment via a dial or button. The airtight seal ensures consistent aspiration and dispensing. Proper technique‚ such as holding the pipette vertically and using the correct tip size‚ is crucial for accuracy. Regular calibration maintains precision‚ ensuring reliable acid volume measurements in laboratory settings.
2.3 Calibration and Maintenance
Regular calibration ensures pipettes deliver accurate volumes‚ crucial for precise acid measurements. Calibration involves adjusting the pipette to ensure it dispenses the correct volume. Maintenance includes cleaning and replacing worn seals or O-rings. Proper storage in a dry‚ upright position prevents contamination. Training on correct usage and scheduling routine calibration services by professionals help maintain performance. Following manufacturer guidelines extends the lifespan and reliability of pipettes in laboratory settings‚ ensuring consistent and accurate results in acid volume measurements.
2.4 Advantages in Acid Measurement
Pipettes offer high precision and accuracy when measuring acid volumes‚ reducing errors in titrations and reactions. Their ability to handle small‚ exact amounts makes them ideal for concentrated acids. Adjustable models allow flexibility in measuring various acid volumes. Pipettes minimize contamination risks compared to other instruments‚ ensuring pure acid solutions. Their ergonomic design reduces fatigue during prolonged use‚ enhancing efficiency in laboratory workflows. Overall‚ pipettes are indispensable tools for accurate and safe acid volume measurement in both research and industrial settings.
2.5 Common Errors and Solutions
Common errors in pipette use include improper technique‚ such as not holding the pipette correctly or failing to calibrate it regularly. Using the wrong pipette size for the volume needed can lead to inaccuracies. Additionally‚ not reading the meniscus correctly or allowing the liquid to drain too slowly can cause errors. Solutions include proper training‚ regular calibration‚ and selecting the right pipette for the task. Ensuring consistent reading techniques and avoiding delays during measurement also improves accuracy. Addressing these issues helps minimize errors and ensures precise acid volume measurement.

Burettes
Burettes are essential volumetric tools for precise acid-base titrations‚ offering a 50 mL measurement range. They deliver accurate volumes through controlled release‚ ensuring reliable experimental outcomes.
3.1 Construction and Function
A burette is a cylindrical glass tube with graduated markings‚ enabling precise volume measurement. It features a stopcock for controlled liquid release and a reservoir for acid solutions. Designed for titrations‚ burettes allow accurate delivery of measured volumes‚ with markings indicating the liquid level. The 0.0 mL mark is typically at the top‚ ensuring precise recordings. This setup enables users to measure and dispense acids accurately‚ making burettes indispensable in acid-base titrations and other analytical procedures requiring exact volume control.
3.2 Titration Techniques
In titration‚ burettes are used to measure precise volumes of acids or bases for neutralization reactions. The process involves filling the burette with the acid solution and setting the initial volume to 0.0 mL. The solution is then slowly released into a flask containing the base‚ and the reaction progress is monitored. The endpoint is determined by a color change using an indicator. Final volume readings are recorded to calculate the exact volume of acid used. This method ensures accuracy in determining concentrations and is widely used in analytical chemistry for precise acid measurements.
3.3 Calibration Procedures
Calibration of burettes is essential for accurate volume measurements. The process starts with rinsing the burette with distilled water. A small amount of water is drawn and discarded to ensure the burette is moisture-free. The burette is then filled with water‚ and the initial volume is recorded. Water is released to the 0.0 mL mark‚ and the final volume is noted. This procedure verifies the burette’s accuracy. Regular calibration ensures precise measurements‚ especially when handling acids‚ where small errors can lead to significant discrepancies in reaction results and concentrations. Proper maintenance prolongs the burette’s reliability and performance.
3.4 Handling Acids Safely
Handling acids requires strict safety protocols to prevent accidents. Always wear protective gear‚ including gloves‚ goggles‚ and lab coats‚ to avoid skin and eye contact. Use glassware instead of plastic‚ as acids can corrode certain materials. Ensure proper ventilation in the lab to avoid inhaling fumes. When measuring acids‚ pour slowly and avoid splashing. In case of spills‚ neutralize with a suitable base and clean immediately. Never handle hot equipment without tongs or clamps. Regular training and adherence to safety guidelines are essential to minimize risks and ensure safe acid handling during volume measurements.
3.5 Reducing Measurement Errors
To minimize errors when measuring acid volumes with burettes‚ ensure proper calibration and use titration techniques accurately. Always read the meniscus level correctly‚ avoiding parallax errors. Use glassware suitable for acidic solutions to prevent corrosion. Regularly clean and maintain equipment to ensure precision. Handle acids carefully‚ avoiding spills and contamination. Use pipettes for transferring acids to burettes to maintain accuracy. Record measurements promptly and double-check calculations. By following these practices‚ you can achieve precise and reliable results in acid volume measurements.

Volumetric Flasks
Volumetric flasks are essential for precise volume measurements. They feature a single calibration mark for accuracy‚ making them ideal for preparing and storing acid solutions.
4.1 Design and Usage
Volumetric flasks are designed with a single calibration mark‚ ensuring precise volume measurements. They are used to prepare and store acid solutions with high accuracy. Made from glass or plastic‚ these flasks feature a narrow neck for easy viewing of the liquid level. The flask is filled to the calibration mark‚ ensuring the exact volume is achieved. They are essential for titrations and dilutions‚ providing consistent results. Proper handling and storage are crucial to maintain their accuracy and longevity in laboratory settings.
4.2 Volume Markings and Accuracy
Volumetric flasks feature a single calibration mark‚ ensuring precise measurement of a specific volume. The mark indicates the exact level to which the liquid should be filled for accuracy. Typically‚ these flasks are calibrated to contain a precise volume‚ such as 100 mL or 1 L‚ with an accuracy of ±0.2 mL. The design ensures minimal error when used correctly. Proper handling‚ such as using a meniscus‚ is essential to achieve the desired precision. These flasks are ideal for preparing standard solutions‚ making them a cornerstone in acid and base titrations for consistent results.
4.3 Storage and Maintenance Tips
Volumetric flasks should be stored upright in a clean‚ dry place to prevent contamination. Avoid exposure to extreme temperatures or corrosive substances‚ as this can affect calibration. After use‚ rinse thoroughly with distilled water and dry with a lint-free cloth. Do not invert flasks‚ as this can damage the neck or calibration mark. Regularly inspect for scratches or etching‚ which may compromise accuracy. For long-term storage‚ protect flasks from dust and physical stress. Proper maintenance ensures longevity and precise measurements‚ essential for accurate acid volume determination.
4.4 Role in Acid Solution Preparation
Volumetric flasks are essential for preparing acid solutions with precise concentrations. They allow accurate measurement of solvents or acids to a specific volume‚ ensuring consistent dilutions. Fill the flask to the calibration mark for precise volume control. This ensures the acid solution meets the required concentration for experiments or reactions. Regular use in acid preparation highlights their importance in maintaining accuracy and safety in laboratory procedures. Proper handling and filling techniques are crucial for reliable results in acid-based solutions.
4.5 Avoiding Common Mistakes
When using volumetric flasks for acid solutions‚ common errors include incorrect filling‚ improper handling‚ and ignoring calibration marks. Always ensure the flask is clean and dry before use. Avoid overfilling or underfilling‚ as this leads to concentration inaccuracies. Never measure acids directly with the flask; instead‚ use pipettes for precise transfer. Secure the flask properly to prevent spills. Regular calibration checks can minimize errors. Following these guidelines ensures accurate and safe preparation of acid solutions‚ maintaining experimental integrity and laboratory safety standards. Proper techniques are crucial for reliable results. Consistency is key in all steps.
Graduated Cylinders
Graduated cylinders are versatile tools for measuring liquid volumes‚ ideal for acids. They feature clear markings and are suitable for various laboratory applications and accurate dispensing.
5.1 Capacity and Measurement Range
Graduated cylinders are available in various capacities‚ typically ranging from 10 mL to 2000 mL‚ ensuring versatility for different laboratory needs. The markings on the cylinder indicate precise volume measurements‚ allowing users to accurately measure and dispense liquids. Constructed from materials like glass or durable plastics‚ they are designed to withstand regular use. The choice of cylinder size depends on the volume of acid to be measured‚ with smaller cylinders offering better precision for low volumes and larger ones suited for bulk measurements. Proper size selection minimizes errors and ensures efficient handling of acidic solutions.
5.2 Reading and Interpreting Markings
Reading graduated cylinders accurately requires attention to detail. The markings indicate specific volumes‚ and the bottom of the meniscus should align with the desired mark. For acids‚ ensure the cylinder is placed on a stable surface and viewed at eye level to avoid parallax errors. The scale typically starts from the bottom‚ with each line representing a specific milliliter increment. Users should note the smallest division to estimate intermediate volumes. Proper interpretation of these markings ensures precise measurement‚ crucial for accurate titrations and solution preparations involving acids.
5.3 Cleaning and Storage Practices
Proper cleaning and storage of graduated cylinders are essential for maintaining accuracy and longevity. After use‚ rinse thoroughly with distilled water to remove any acid residues. For tougher stains‚ mild detergent solutions may be used‚ but avoid abrasive materials that could scratch the glass. Dry the cylinder with a lint-free cloth to prevent water spots. Store in a dry‚ upright position to avoid dust accumulation. Never store acids in graduated cylinders‚ as they are designed for measurement‚ not storage. Regular cleaning ensures precise measurements and prevents contamination‚ crucial when working with corrosive substances like acids.
5.4 Suitability for Acid Volumes
Graduated cylinders are suitable for measuring acid volumes due to their durable construction and clear markings. They are ideal for handling corrosive substances when made from materials like borosilicate glass or plastic. However‚ they are not as precise as pipettes or burettes for small volumes. Regular rinsing with distilled water after use prevents acid residues from affecting future measurements. While they can measure a wide range of acid volumes‚ they are best used for larger quantities where high precision is not critical. Proper handling ensures safe and accurate acid volume measurement.
5.5 Minimizing Errors in Use
To minimize errors when using graduated cylinders for measuring acid volumes‚ ensure stability on a flat surface and read the meniscus at eye level for accuracy. Clean the cylinder thoroughly before and after use to prevent contamination. Select a cylinder made from acid-resistant materials like borosilicate glass or durable plastics. Choose an appropriate size relative to the volume needed to avoid multiple transfers and ensure precise measurements. Follow lab protocols for handling acids‚ including proper calibration checks of the cylinder. Wear appropriate PPE such as gloves‚ goggles‚ and lab coats to handle acids safely and maintain a controlled environment. Regular calibration ensures the volume markings remain accurate‚ reducing measurement errors. Proper storage and labeling of the cylinder after use prevent mix-ups and maintain consistency in future measurements. By adhering to these guidelines‚ you can enhance accuracy and safety when measuring acid volumes with graduated cylinders.
Titration Systems
Titrations systems enable precise measurement of acid concentrations through automated or manual processes. They utilize components like burettes and sensors for accurate acid-base reactions and monitoring.
6.1 Automated vs. Manual Titration
Automated titration systems offer high precision and efficiency‚ reducing human error and saving time‚ especially in high-throughput environments. Manual titration‚ while cost-effective‚ requires skill and attention to detail‚ making it suitable for smaller-scale operations. Automated systems often include advanced features like data logging and real-time monitoring‚ enhancing accuracy and reproducibility. Manual methods rely on operator expertise‚ making them less consistent but still valuable for specific applications. The choice between automated and manual titration depends on laboratory needs‚ budget‚ and the desired level of precision for acid volume measurements.
6.2 Components and Setup
A titration system typically includes a burette or titrant reservoir‚ a detection mechanism such as a pH electrode‚ and a control unit or software; Automated systems may also incorporate stirrers and temperature sensors. The burette is filled with the titrant‚ and the analyte is placed in a flask below. The system is connected to a computer for data recording. Manual setups rely on visual indicators like color change. Proper setup ensures accurate delivery and detection‚ minimizing errors in acid volume measurement. Calibration of components is essential for precise results in both automated and manual configurations.
6.3 Calibrating the System
Calibrating a titration system ensures accuracy in acid volume measurements. Standard solutions of known concentration are used to verify the system’s precision. Automated systems may self-calibrate‚ while manual systems require careful adjustment. The burette and detection mechanisms‚ such as pH electrodes‚ must be aligned and tested. Regular calibration prevents drift and ensures reliable results. Proper calibration involves checking the system’s response to known acid concentrations and adjusting settings accordingly. This step is critical for maintaining precision and consistency in titration experiments‚ especially when handling corrosive or volatile acids. Regular maintenance and recalibration are essential for optimal performance.
6.4 Monitoring Acid Concentration
Monitoring acid concentration during titration is essential for precise volume measurements. Sensors and detection systems‚ such as pH electrodes or conductivity probes‚ track changes in solution properties. Automated titrators continuously monitor and adjust the acid concentration‚ ensuring accurate endpoint detection. Manual systems rely on visual indicators like color changes. Real-time data allows for precise control‚ reducing errors. This step ensures the solution reaches the desired concentration‚ critical for accurate volume measurements. Regular sensor calibration and maintenance are necessary for reliable results. Proper monitoring enhances efficiency and consistency in acid concentration management during titration processes.
6.5 Maintenance for Optimal Performance
Regular maintenance is crucial for titration systems to ensure accuracy and longevity. Cleaning components like burettes and valves with distilled water prevents chemical residue buildup. Lubricating moving parts reduces wear and tear. Calibration should be performed periodically to align measurements with standards. Replacing worn-out seals and damaged tubing maintains system integrity. Proper storage in a dry‚ cool environment prevents corrosion. Following manufacturer guidelines ensures optimal performance. Consistent upkeep minimizes downtime and enhances precision‚ making maintenance a vital part of reliable acid volume measurement processes.
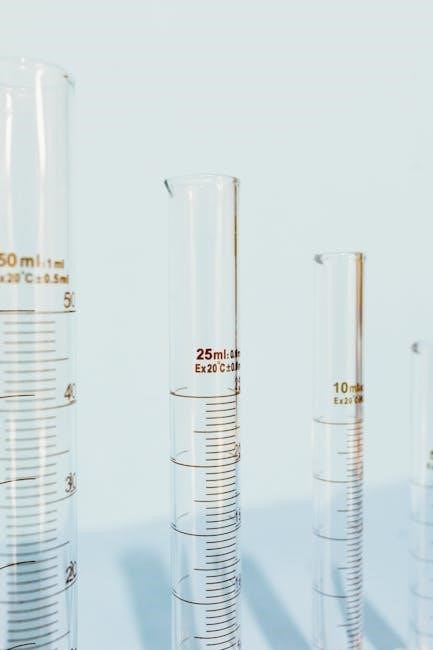

Comparing Measurement Instruments
Comparing instruments like pipettes‚ burettes‚ and volumetric flasks helps determine their accuracy‚ volume range‚ and suitability for specific acid measurement tasks‚ ensuring optimal equipment selection.
7.1 Accuracy Levels Across Devices
Accuracy varies among laboratory instruments. Pipettes typically offer ±0.1% precision‚ ideal for precise acid measurements; Burettes provide accurate titration with ±0.1 mL errors. Graduated cylinders are less accurate‚ suitable for larger volumes‚ while volumetric flasks ensure ±0.1 mL precision for solution preparation. Understanding each device’s accuracy is crucial for selecting the right tool‚ ensuring reliable results in acid volume measurements and maintaining experimental integrity across various applications.
7.2 Volume Range and Appropriateness
The choice of equipment depends on the required volume and precision. Pipettes are ideal for small‚ precise measurements (0.1 µL to 10 mL)‚ while burettes handle larger volumes (up to 50 mL) during titrations. Graduated cylinders measure broader ranges (10 mL to 2 L) but are less precise. Volumetric flasks are perfect for preparing exact volumes (e.g.‚ 1 L) with high accuracy. Selecting the right instrument ensures efficient and accurate acid volume measurement‚ avoiding unnecessary errors in experiments.
7.3 Cost Considerations
Cost plays a significant role in selecting equipment for measuring acid volumes. Pipettes‚ while precise‚ can be expensive‚ especially high-accuracy models. Volumetric flasks and graduated cylinders are more budget-friendly‚ offering good value for routine measurements. Burettes are cost-effective for titration purposes. Automated titration systems are pricey but efficient for high-throughput labs. Budget constraints may lead to choosing standard equipment over premium options. However‚ investing in durable‚ high-quality instruments reduces long-term costs and ensures reliability. Balancing accuracy needs with budget is crucial for optimal resource utilization in laboratory settings.
7.4 User-Friendliness and Efficiency
User-friendliness and efficiency are key factors in selecting equipment for measuring acid volumes. Pipettes are highly efficient for precise measurements and are ergonomically designed for comfortable use. Burettes offer straightforward operation for titration‚ while volumetric flasks and graduated cylinders are simple to read and handle. Automated titration systems enhance speed and reduce manual effort‚ making them ideal for high-throughput labs. The design of these instruments often includes features like intuitive controls and clear markings‚ ensuring ease of use and minimizing errors. Efficiency and ease of operation are critical for maintaining productivity in laboratory settings;
Safety and Best Practices
Safety is paramount when handling acids. Always wear PPE‚ including gloves and goggles‚ to prevent skin and eye contact. Ensure proper ventilation and avoid inhaling fumes.
8.1 Handling Corrosive Acids Safely
Handling corrosive acids requires extreme caution to prevent accidents. Always wear PPE‚ including gloves‚ goggles‚ and a lab coat‚ to avoid skin and eye contact. Ensure acids are stored in sealed‚ labeled containers and handled in well-ventilated areas or fume hoods to minimize inhalation of vapors. Use secondary containment to prevent spills from spreading. Keep neutralization kits nearby for emergencies. Never pour acid into water; instead‚ add water slowly to the acid. Follow proper cleanup procedures and dispose of waste according to safety protocols. Regular training and familiarity with emergency protocols are essential for safe handling.
8.2 Using PPE Effectively
Using PPE effectively is crucial when handling acids. Wear lab coats‚ acid-resistant gloves‚ and closed-toe shoes to protect skin from splashes. Safety goggles or face shields guard eyes from chemical exposure. Ensure all PPE fits properly and is free from damage. Replace worn-out items immediately. Tie back long hair and avoid loose jewelry to prevent entanglement. Familiarize yourself with PPE guidelines and inspect items before use. Properly remove and dispose of PPE after handling acids to prevent cross-contamination. Regular training on PPE usage ensures compliance with safety standards‚ reducing accident risks and enhancing workplace safety.
8.3 Preventing Cross-Contamination
Preventing cross-contamination is vital when handling acids to maintain sample integrity and safety. Always use dedicated equipment for acidic solutions to avoid residue transfer. Ensure all tools like pipettes‚ burettes‚ and flasks are thoroughly cleaned with deionized water and dried between uses. Regularly calibrate and maintain equipment to prevent chemical carryover. Store acids in clearly labeled‚ separate areas to avoid mix-ups. Follow standardized cleaning protocols and use disposable gloves when handling multiple substances. Training staff on proper techniques and protocols minimizes contamination risks‚ ensuring accurate measurements and a safer working environment. Regular audits and checks further reinforce these practices.
8.4 Emergency Procedures
In case of acid spills or exposure‚ act swiftly to minimize risks. Evacuate the area if a large spill occurs and alert others. For skin contact‚ immediately rinse with plenty of water for at least 15 minutes. Flush eyes with water for 10-15 minutes if exposed. Neutralize spills with sodium bicarbonate or sodium carbonate‚ then clean thoroughly. Keep emergency showers and eyewash stations accessible. Store acids in well-ventilated areas and have a fire extinguisher nearby. Dispose of contaminated materials safely. Always have a first aid kit on hand and seek medical attention if necessary. Training on emergency protocols is essential for all personnel.
Accurate measurement of acid volumes is vital for precise chemical reactions and safety. Using appropriate equipment like pipettes‚ burettes‚ and volumetric flasks ensures reliable results and minimizes risks.
9.1 Recap of Key Equipment
Key equipment for measuring acid volumes includes pipettes‚ burettes‚ volumetric flasks‚ and graduated cylinders. Pipettes deliver precise volumes‚ while burettes are ideal for titrations. Volumetric flasks ensure accurate solution preparation‚ and graduated cylinders measure larger quantities. Each tool has specific functions‚ ensuring accuracy and safety. Proper selection and maintenance of this equipment are crucial for achieving reliable results in chemical analyses. Understanding their roles enhances laboratory efficiency and data consistency.
9.2 Final Tips for Precise Measurements
For precise acid volume measurements‚ always calibrate equipment regularly and use the appropriate tool for the task. Ensure proper handling of acids‚ wearing PPE‚ and maintaining a clean workspace. Read menisci accurately‚ avoid parallax errors‚ and document measurements clearly. Regularly inspect and maintain instruments to prevent wear and tear. Follow safety protocols to minimize risks. Consistent practice and attention to detail will enhance accuracy and reliability in laboratory procedures. By adhering to these guidelines‚ you ensure precise and safe measurement of acid volumes in various applications.